By
Jing Wu et al.
Source ASM
ABSTRACT
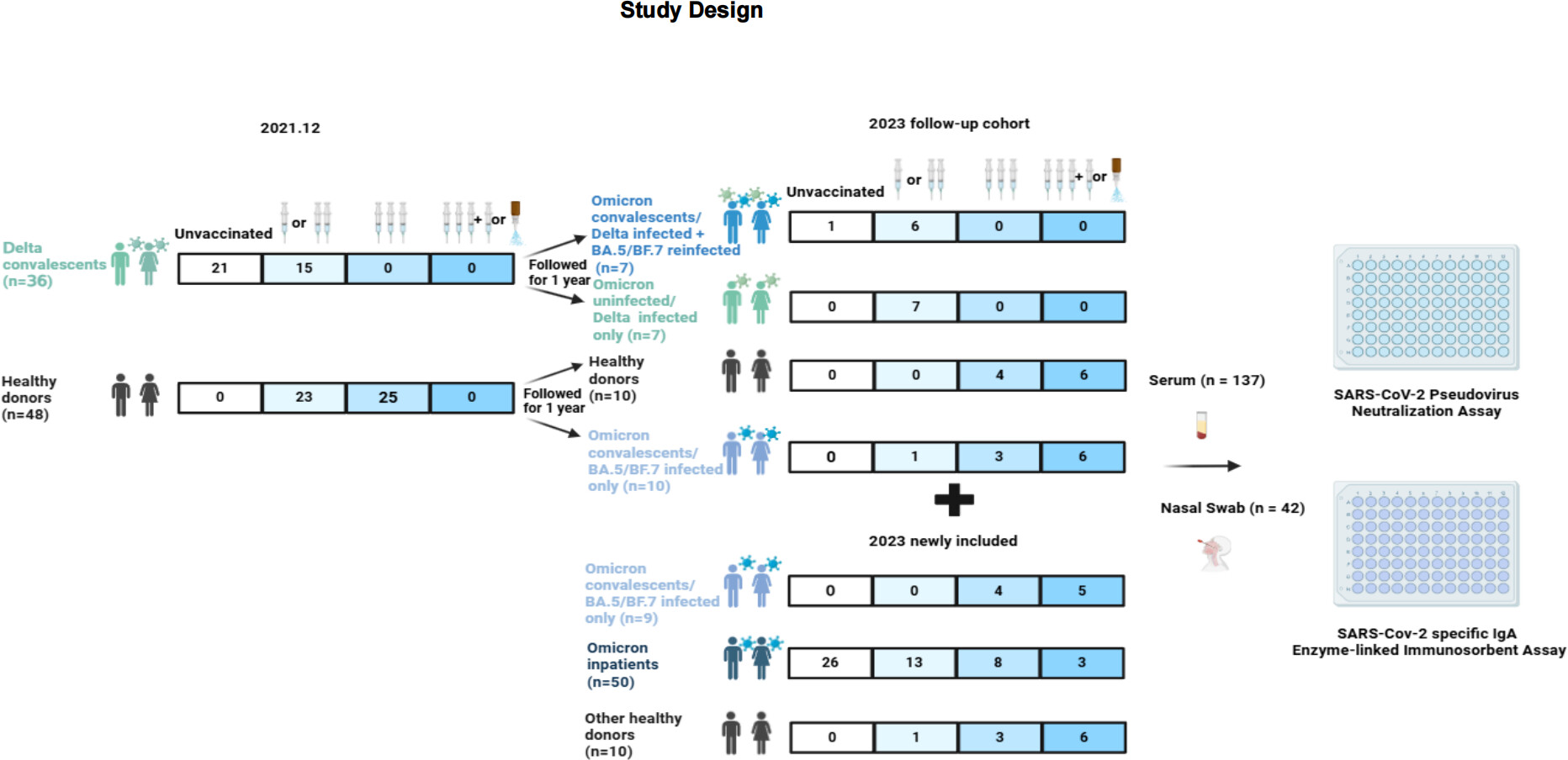
It remains unclear how previous infections and vaccinations influenced and shaped heterogeneous immune responses against Omicron and its variants in diverse populations in China. After the national wave of Omicron in early 2023, we evaluated serum levels of neutralizing antibodies (nAbs) against Omicron (B.1.1.529) and its variants (BA.5, BF.7, and CH1.1) in 33 COVID-19 convalescents and 40 uninfected vaccinees, using vesicular stomatitis virus-based pseudovirus neutralizing assay. In addition, we followed 34 Delta convalescent patients to compare their immune responses against Omicron before (late 2021) and after the Omicron wave (early 2023). NAbs at the acute phase of the disease were investigated in 50 Omicron inpatients, including 24 vaccinated and 26 unvaccinated patients. Among them, nasal mucosal IgA levels were measured in 42 subjects. Compared to vaccination, breakthrough infections significantly increased the breadth and magnitude of serum nAbs and mucosal IgA levels against Omicron variants. Exposure to Omicron but not Delta elicited stronger pan-Omicron responses. In Omicron inpatients, nAbs continued to rise as vaccination doses increased. However, in both vaccinees and convalescents, a fourth dose vaccination did not elicit higher nAbs against Omicron. Furthermore, nAbs against Omicron variants lasted longer than nAbs against WT SARS-CoV-2. Breakthrough infections of Omicron variants elicited specific immune responses against Omicron compared to vaccination and Delta infection. Although repeated vaccination revealed limited impacts on serum nAbs, populations at high risk of hospitalization may still benefit from continued vaccination.