By Anna Shteinfer‑Kuzmine et al.
Source Springer Link
Abstract
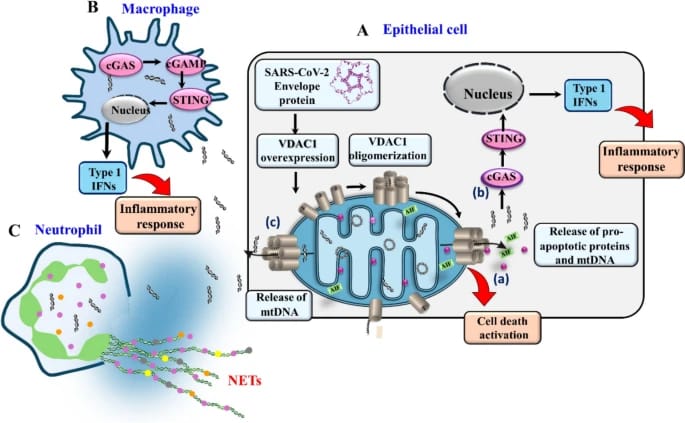
Mitochondria dysfunction is implicated in cell death, inflammation, and autoimmunity. During viral infections, some viruses employ different strategies to disrupt mitochondria-dependent apoptosis, while others, including SARS-CoV-2, induce host cell apoptosis to facilitate replication and immune system modulation. Given mitochondrial DNAs (mtDNA) role as a pro-inflammatory damage-associated molecular pattern in inflammatory diseases, we examined its levels in the serum of COVID-19 patients and found it to be high relative to levels in healthy donors. Furthermore, comparison of serum protein profiles between healthy individuals and SARS-CoV-2-infected patients revealed unique bands in the COVID-19 patients. Using mass spectroscopy, we identified over 15 proteins, whose levels in the serum of COVID-19 patients were 4- to 780-fold higher. As mtDNA release from the mitochondria is mediated by the oligomeric form of the mitochondrial-gatekeeper—the voltage-dependent anion-selective channel 1 (VDAC1)—we investigated whether SARS-CoV-2 protein alters VDAC1 expression. Among the three selected SARS-CoV-2 proteins, small envelope (E), nucleocapsid (N), and accessory 3b proteins, the E-protein induced VDAC1 overexpression, VDAC1 oligomerization, cell death, and mtDNA release.
Researchers suggest that COVID-19 pathology is associated with the induction of VDAC1 overexpression and oligomerization, leading to cell death and the release of mitochondrial vfmtDNA, which is associated with the cytokine storm that directly influences SARS-CoV-2 severity and the COVID-19 illness.
E PROTEIN hence induced MITOCHONDRIAL DYSFUNCTION and apoptosis, leading to HIGH LEVELS of MITOCHONDRIA FRAGMENTS in the BLOOD 😨 – key pathways contributing to COVID-19 severity.
電壓依賴性陰離子選擇性通道1(VDAC1)是一種β桶蛋白,在人類中是由5號染色體上的VDAC1基因所製造[4][5]。此蛋白質會在線粒體外膜(OMM)和細胞膜中形成離子通道:在OMM上,ATP通過該離子通道而能自線粒體擴散至細胞質;在細胞膜中,VDAC1則參與體積的調節。
Read more click here