By Ewa Moliszewska rt al.
Source Nature
中國新冠大流行,過敏性鼻炎加增
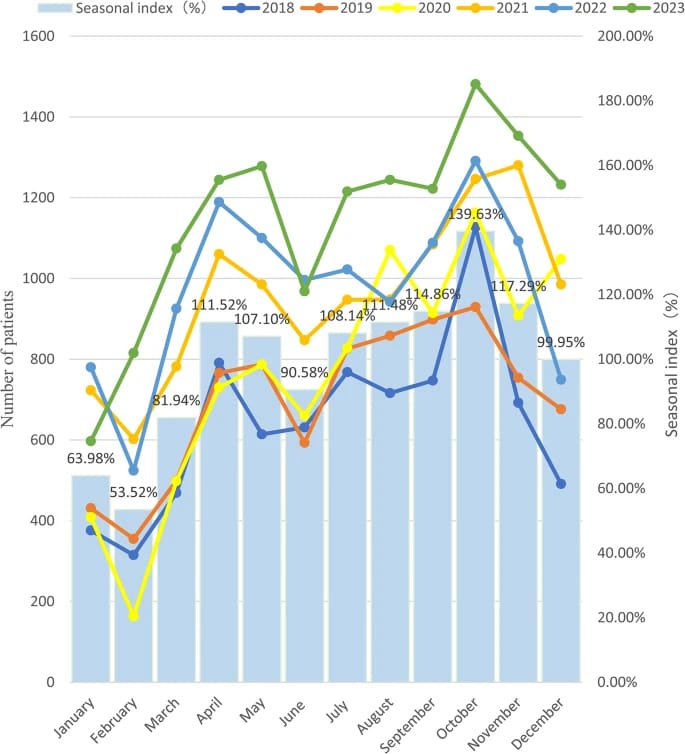
From a China study using local big data of patients with allergic rhinitis (AR) in from 2018 to 2023, AR is a non-infectious inflammatory disease of the nasal mucosa, which occurs after the body is exposed to allergens and is mainly mediated by immunoglobulin E (IgE).
AR can develop at a relatively young age, reduce quality of life, and the socioeconomic burden is increasing worldwide.
This study showed that the prevalence of AR increased year by year.
COVID-19 appears to have accelerated the annual increase in prevalence of AR.
The symbiotic flora will be unbalanced with the combination of SARS-CoV-2 virus and ACE2 receptors present in the nasal mucosa.
It can cause inflammation, induce allergy, and increase the prevalence of AR.
Because SARS-CoV-2 virus and COVID-19 mRNA vaccines have relatively large protein sequences homologous to grass pollen, dust mite and mold, therefore, infection with SARS-CoV-2 virus and vaccination against COVID-19 may promote T cell cross-reactivity with allergens that affect allergic rhinitis.
Read more click here